Recommendation Engine of movies
Project: https://github.com/octadelsueldo/recommendation_engine
Objective
We will show how to build recommendation engines using Alternating Least Squares in PySpark.
Target
We will look forward to the minimum RMSE which means, on average, how far is our predictions from the real values.
Data
This dataset (ml-latest) describes a 5-star rating and free-text tagging activity from MovieLens, a movie recommendation service. It contains 27,753,444 ratings and 1,108,997 tag applications across 58098 movies. These data were created by 283228 users between January 09, 1995, and September 26, 2018. This dataset was generated on September 26, 2018.
Users were selected at random for inclusion. All selected users had rated at least 1 movie. No demographic information is included. Each user is represented by an id, and no other information is provided.
EDA
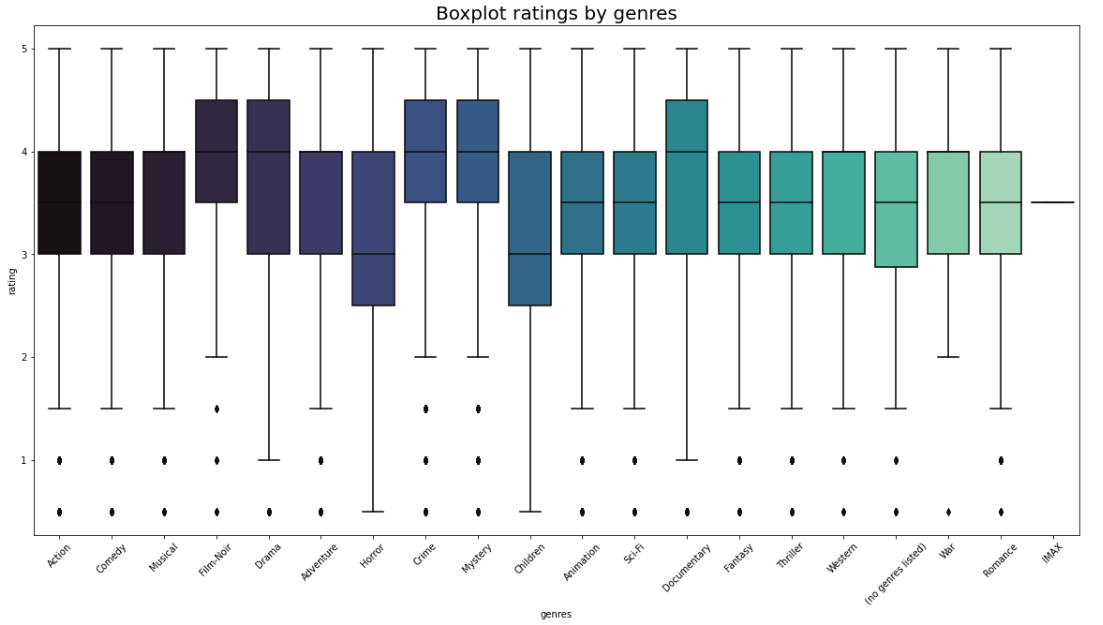
In this part, we have performed the EDA, so we can see more details of these datasets. First of all, we will look up the first and last rows, get the data shape, schema, dictionary of the variables... Also, we have studied if we have to drop some variables, study NaN and duplicate data. In addition to this, we have performed a genre analysis to know which of the different genres are most rated, better-rated, or their distributions. Also, we studied movies without genres listed. Plus, we studied the most popular movies, movies not rated, the number of movies by year, etc. Finally, we perform an analysis of different users of our interest.
Processing data
In order to perform the algorithm, we have processed the data and created our TRAIN, VALIDATION, and TEST datasets.
Predictions
| Algorithm | RMSE |
|---|---|
| ALS | 0.81328 |
Conclusions
We learned that matrix factorization can solve “popular bias” and “item cold-start” problems in collaborative filtering. We also leveraged Spark ML to implement distributed recommender system using Alternating Least Square (ALS)
Repository structure
README.md <- The top-level README for developers.
data
01_raw <- Immutable input data
02_models <- trained models
html <- html of the notebooks.
notebooks <- Jupyter notebooks.
references <- Data dictionaries, manuals, etc.
requirements.txt <- The requirements file for reproducing the analysis environment.
.gitignore <- Avoids uploading data, credentials, outputs, system files etc
Authors:
Octavio del Sueldo hugo.delsueldo@cunef.edu
Jose López Galdón jose.lopez@cunef.edu
